-
Table of Contents

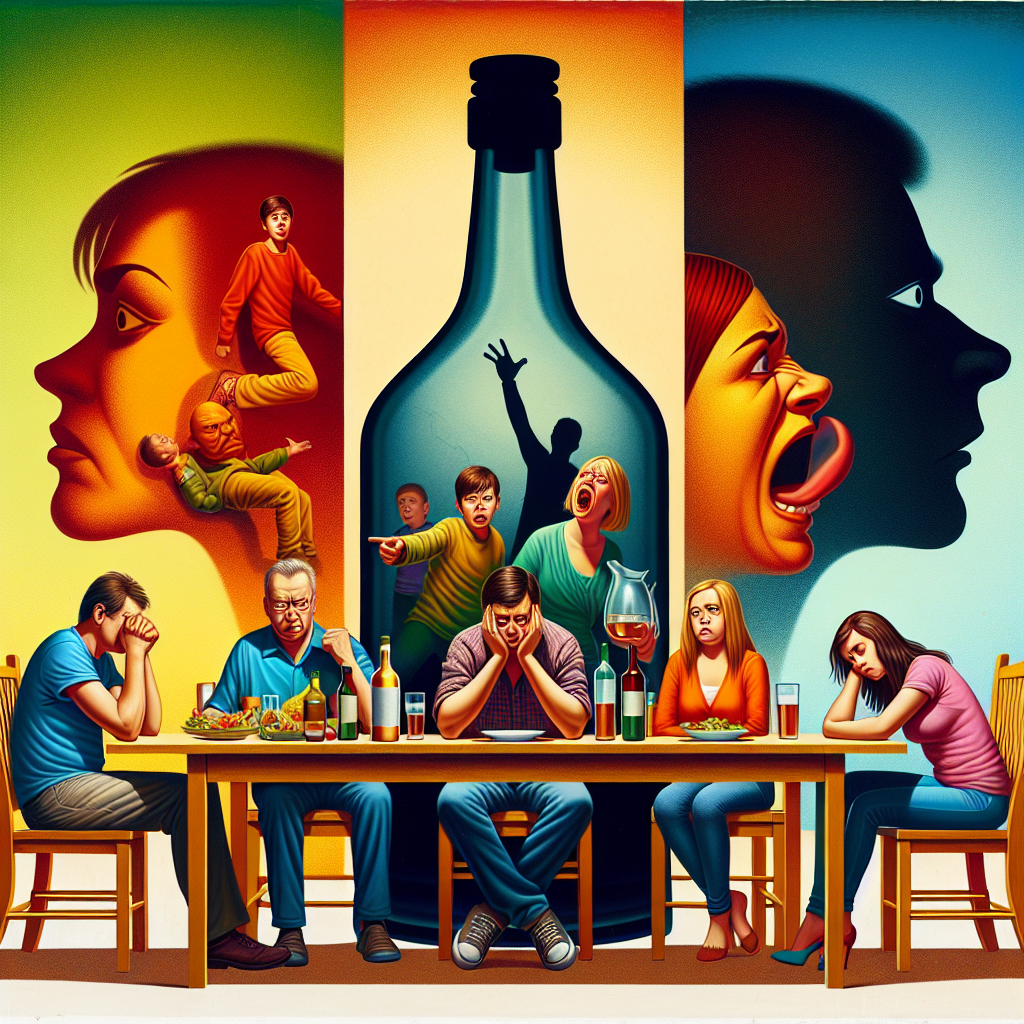
“Shattered Bonds: The Ripple Effect of Alcoholism on Family Dynamics”
Introduction
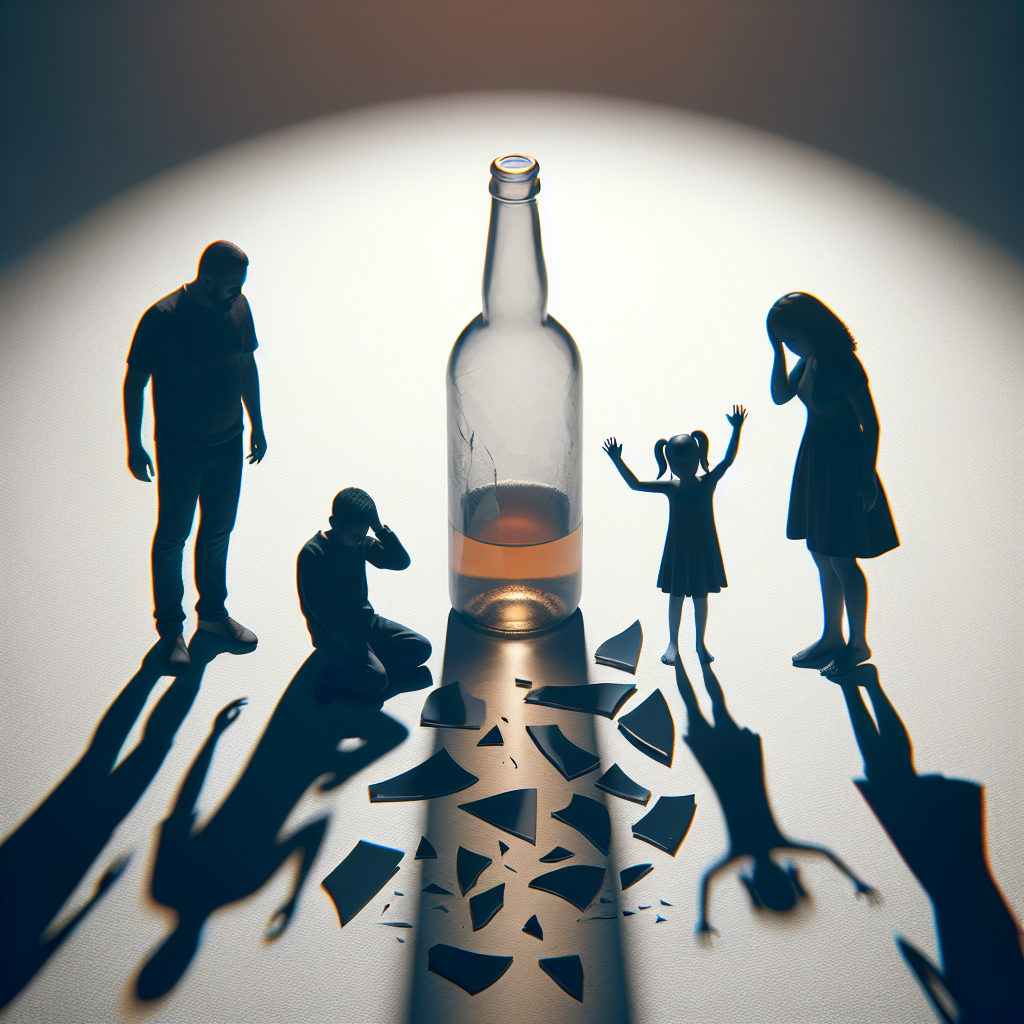
Alcoholism, a chronic and often progressive disease characterized by an inability to control alcohol consumption despite adverse consequences, profoundly affects not only the individual but also their family. The impact of alcoholism on family dynamics is multifaceted, influencing emotional, psychological, and social aspects of family life. Families dealing with alcoholism often experience heightened levels of stress, conflict, and instability, which can lead to long-term emotional and behavioral issues among family members. Children in these environments are particularly vulnerable, facing increased risks of neglect, abuse, and developmental problems. The strain on marital relationships can result in separation or divorce, further disrupting the family unit. Understanding the complex interplay between alcoholism and family dynamics is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems to mitigate these adverse effects and promote healthier family environments.
The Emotional Toll of Alcoholism on Family Members
Alcoholism, a pervasive and destructive force, extends its reach far beyond the individual suffering from addiction. The emotional toll it takes on family members is profound and multifaceted, often leaving lasting scars. Understanding the emotional impact of alcoholism on families is crucial in fostering empathy and support for those affected.
Initially, the emotional landscape of a family dealing with alcoholism is often characterized by confusion and denial. Family members may struggle to comprehend the changes in their loved one’s behavior, attributing it to stress or temporary issues. This denial can be a coping mechanism, a way to shield themselves from the painful reality. However, as the addiction progresses, denial becomes increasingly untenable, giving way to a tumultuous mix of emotions.
Fear and anxiety soon become constant companions for family members. The unpredictability of an alcoholic’s behavior creates an environment of instability and insecurity. Children, in particular, may feel a heightened sense of fear, unsure of what to expect from one day to the next. This chronic anxiety can lead to long-term psychological effects, including depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Simultaneously, feelings of guilt and shame often permeate the family dynamic. Spouses and children may blame themselves for their loved one’s addiction, believing that they could have done something to prevent it. This self-blame is exacerbated by societal stigma surrounding alcoholism, which can isolate families and prevent them from seeking the help they desperately need. The weight of this guilt can be overwhelming, leading to a sense of hopelessness and despair.
Moreover, anger and resentment frequently surface as family members grapple with the consequences of alcoholism. The broken promises, financial strain, and emotional neglect that often accompany addiction can erode trust and breed bitterness. This anger, while a natural response, can further fracture family relationships, creating a cycle of conflict and estrangement. It is essential for families to recognize these emotions and seek healthy ways to address them, rather than allowing them to fester and cause further harm.
Despite the myriad challenges, it is important to acknowledge the resilience and strength that families can exhibit in the face of alcoholism. Many families find ways to support their loved one while also taking care of their own emotional well-being. This often involves setting boundaries, seeking therapy, and connecting with support groups. These steps can help family members reclaim a sense of control and foster a more positive and supportive environment.
In addition, the journey through alcoholism can sometimes lead to profound personal growth and stronger family bonds. As families navigate the complexities of addiction, they may develop a deeper understanding of each other’s struggles and strengths. This shared experience can create a sense of solidarity and mutual support, ultimately leading to a more resilient family unit.
In conclusion, the emotional toll of alcoholism on family members is significant and multifaceted, encompassing fear, guilt, anger, and resilience. By acknowledging and addressing these emotions, families can begin to heal and support their loved one’s recovery journey. It is through empathy, understanding, and a commitment to self-care that families can navigate the challenges of alcoholism and emerge stronger on the other side.
Coping Strategies for Families Affected by Alcoholism
Coping with the impact of alcoholism on family dynamics can be an overwhelming and emotionally taxing experience. However, understanding and implementing effective coping strategies can help families navigate these challenges and foster a supportive environment for everyone involved. One of the first steps in coping with alcoholism within the family is to educate oneself about the nature of the disease. Recognizing that alcoholism is a chronic condition that affects both the mind and body can help family members approach the situation with empathy and compassion, rather than judgment and frustration.
Communication plays a crucial role in managing the effects of alcoholism on family dynamics. Open, honest, and non-confrontational dialogue can help family members express their feelings and concerns without escalating tensions. It is essential to create a safe space where everyone feels heard and understood. This can be achieved by setting aside regular times for family meetings, where each person has the opportunity to speak and listen. Additionally, using “I” statements rather than “you” statements can help prevent defensiveness and promote constructive conversations.
Seeking professional help is another vital coping strategy for families affected by alcoholism. Therapists, counselors, and support groups can provide valuable guidance and resources. Family therapy, in particular, can help address underlying issues and improve communication and relationships within the family unit. Support groups such as Al-Anon offer a community of individuals who share similar experiences, providing a sense of solidarity and understanding. These groups can also offer practical advice and coping mechanisms that have been effective for others in similar situations.
Setting boundaries is an essential aspect of coping with alcoholism in the family. It is important for family members to establish clear and consistent boundaries to protect their own well-being. This might include setting limits on behaviors that are unacceptable or harmful, such as verbal abuse or financial exploitation. Enforcing these boundaries can be challenging, but it is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functional family dynamic. It is also important to remember that setting boundaries is not about punishing the person with alcoholism, but rather about protecting oneself and the family as a whole.
Self-care is another critical component of coping with the impact of alcoholism on family dynamics. Family members often become so focused on helping their loved one that they neglect their own needs. Engaging in activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being is essential. This might include exercise, hobbies, spending time with friends, or seeking individual therapy. Taking care of oneself not only helps to manage stress but also sets a positive example for the person struggling with alcoholism.
Lastly, maintaining hope and fostering resilience are key to coping with the challenges of alcoholism within the family. It is important to recognize that recovery is a journey, often marked by setbacks and progress. Celebrating small victories and remaining optimistic about the future can help sustain motivation and perseverance. Encouraging the person with alcoholism to seek treatment and supporting them throughout their recovery process can make a significant difference.
In conclusion, while the impact of alcoholism on family dynamics can be profound, there are effective coping strategies that can help families navigate these challenges. By educating themselves, fostering open communication, seeking professional help, setting boundaries, practicing self-care, and maintaining hope, families can create a supportive and resilient environment. Through these efforts, it is possible to mitigate the negative effects of alcoholism and work towards healing and recovery for everyone involved.
Q&A
1. **Question:** How does alcoholism affect the emotional well-being of family members?
**Answer:** Alcoholism can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression among family members, as they may feel neglected, unsafe, or burdened by the alcoholic’s behavior and the associated unpredictability.
2. **Question:** What are some common behavioral issues in children of alcoholic parents?
**Answer:** Children of alcoholic parents often exhibit behavioral issues such as academic difficulties, social withdrawal, aggression, and a higher likelihood of developing substance abuse problems themselves.
Conclusion
The impact of alcoholism on family dynamics is profound and multifaceted, often leading to emotional, psychological, and financial strain. Alcoholism can disrupt communication, erode trust, and create an environment of instability and unpredictability. Family members may experience feelings of guilt, shame, and helplessness, and children in particular may suffer from neglect or abuse, leading to long-term developmental and emotional issues. The overall family structure can become dysfunctional, with roles and responsibilities becoming blurred or reversed. Effective intervention and support are crucial to mitigate these adverse effects and promote healing and recovery within the family unit.